6 Hormones Involved In The Ovulation Cycle
Surely you have heard something about the effects of hormones on the body, both in men and women. Did you know that, without some of them, the female cycle would not exist? Specifically, we are talking about the 6 hormones involved in the ovulation cycle.
It is thanks to these hormones that we experience a cycle that repeats every month. Do you want to know what hormones are involved in the ovulation cycle? Keep reading.
Hormones involved in the ovulation cycle
Hormones are not unique to humans. They are chemicals that plants and animals also produce.
They intervene in processes of metabolism, growth, development and reproduction. They also influence mood and sexual appetite, among many other aspects.
Hormones are part of the endocrine system, which is responsible for controlling the proper functioning of the body. They function as chemical messengers that travel through the blood.
This is how these small compounds regulate different and important biochemical processes in the body. One of them is the ovulation cycle.
What is ovulation
The release of an egg from an ovary, that is, ovulation, is a process that depends on hormonal changes. It usually occurs once every menstrual cycle, 12 to 16 days before the start of the next menstrual period.
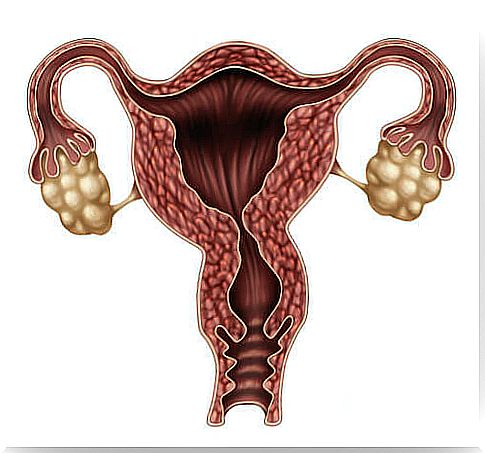
Ovulation occurs thanks to a complex hormonal communication system formed by the hypothalamus, pituitary, ovary and uterus. Specifically, these 6 hormones are involved in the ovulation cycle.
1. Hormones involved in the ovulation cycle: GnRH hormone
The process of ovulation cannot start without the compound known as gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This chemical messenger is synthesized and released in the neurons of the hypothalamus.
In addition to being one of the hormones involved in the ovulation cycle, GnRH is considered a neurohormone since it is produced in a neuronal cell and is released through its nerve endings.
Through the bloodstream, GnRH is conducted to the pituitary gland, where it stimulates the production of substances that participate in the synthesis and secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
In turn, these compounds are controlled by GnRH, estrogens, and androgens. In women, GnRH secretion is not constant. Its frequency changes during the menstrual cycle, and production increases before ovulation.
2. Estrogens
Estrogens are steroids or sex hormones that are produced mainly in the ovaries. These substances are responsible for inducing changes in cell production in the endometrium, breast and ovary.
Some of the functions of estrogens are to regulate the menstrual cycle, and to participate in the development of sexual characteristics in women.
There are different types of natural estrogens: estrone, estradiol, and estriol. However, the predominant one is the estradiol hormone which is briefly explained below.
3. Estradiol
Estradiol is an estrogen, the hormone responsible for the onset of the menstrual cycle. The production of this compound increases during puberty and is usually maintained during the childbearing years until the menopause.
Some specialists classify it as the sex hormone par excellence due to the essential functions it performs. For example, estradiol is responsible for the formation and maintenance of a single mature oocyte in each menstrual cycle.
Likewise, estradiol also participates in the production of luteinizing hormone (LH) through activation signals. In addition, it stimulates the growth of the endometrium and prepares it for conception.
4. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
As its name suggests, the follicle-stimulating hormone is responsible for maturing the follicles, small fluid cavities in which the undeveloped eggs are found. As a result, the eggs mature thanks to stimulation in the ovaries.
It works in conjunction with luteinizing hormone (LH). It is also responsible for stimulating estrogen production and, in general, sexual maturation. In men it is also important, since it is responsible for the maturation of sperm.
As we have said, in the ovulation cycle, FSH begins to be secreted at the beginning of the cycle and acts in the ovaries, maturing the oocytes. At that moment, estradiol begins to be secreted, which blocks the production of FSH when it is no longer needed, so that only one ovum continues.
5. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH) production is stimulated by high levels of estrogen. This hormone, produced by the pituitary, triggers the signal to break the follicle that has matured thanks to the previous hormones.
This process happens when LH reaches peak levels. It is at this point that ovulation itself occurs, that is, the release of the mature ovum from the ovary.
However, luteinizing hormone is also required to synthesize estrogens, and to facilitate follicles to respond to the effects of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
6. Progesterone
Although it participates in other physiological processes, the main function of progesterone is to prepare the uterus for pregnancy.
Just after ovulation, progesterone acts to thicken the layers of the uterus, preparing it to house an egg that succeeds in implanting when fertilized.
If this fact does not occur, then the menstrual phase begins to, again, begin to produce follicles and a mature ovum.
Although progesterone is not one of the hormones that intervenes in the ovulation cycle directly, it does intervene to restart this process.
Hormones involved in the ovulation cycle: hormonal balance is essential
Ovulation is a cycle that depends on different glands and hormones to function properly. This hormonal balance is essential for the proper development of vital functions. If a hormonal imbalance occurs, our body could warn us in different ways.