What Is A Sarcoma?
When we talk about a sarcoma we are talking about a type of cancer. It is an abnormal and malignant growth of cells in certain tissues of the body that multiply uncontrollably.
The tissues that cause sarcomas are bone and the so-called soft tissues of the body. Among these soft tissues we have lipids, muscles, cartilage, blood vessels, among others.
We could say, then, that a sarcoma is a connective tissue cancer. This extensive tissue is also called connective or supporting tissue . Its main characteristic is that it has a lot of extracellular matrix between the cells that form it.
As indicated by the experts of the Spanish Association Against Cancer, sarcomas are not so frequent. Of the total number of cancers that affect humans, it is estimated that less than 1% are sarcomas. And of cancer deaths, 2% are attributed to them.
Although they can appear anywhere on the body, they are more common in the extremities, both legs and arms. They are also present within the cavity of the abdomen and even in the head.
The age of onset is usually between 40 and 70 years. Some varieties are characteristics of childhood and, in general, males are more affected than females.
Causes of sarcoma
As with many cancers, a specific cause of its genesis cannot be established. It is assumed that a number of factors coincide for the tumor to develop and cells to grow uncontrollably.
In the case of sarcomas, it has not even been possible to establish clear risk factors for some varieties, which makes prevention more difficult. Studies are being conducted in the scientific world to reach conclusions about these soft tissue tumors.
With experience and research , a few risk factors have been established :
- Genetic diseases: there are pathologies, such as neurofibromatosis, which, being congenital, have among their symptoms the proliferation of sarcomas.
- Radiation therapy: When a person undergoes radiation therapy as a treatment, either for thyroid problems or for neoplasms, it can have the adverse effect of developing soft tissue tumors.
- Viruses: there are infections that increase the probability of getting sick with sarcomas. Kaposi’s sarcoma, for example, is linked to a variety of herpes.
- Lymphedema: Lymphedema is the accumulation of lymph in the soft parts of the body. When this situation is prolonged in time and becomes chronic, the tissues can proliferate in the form of neoplasia.
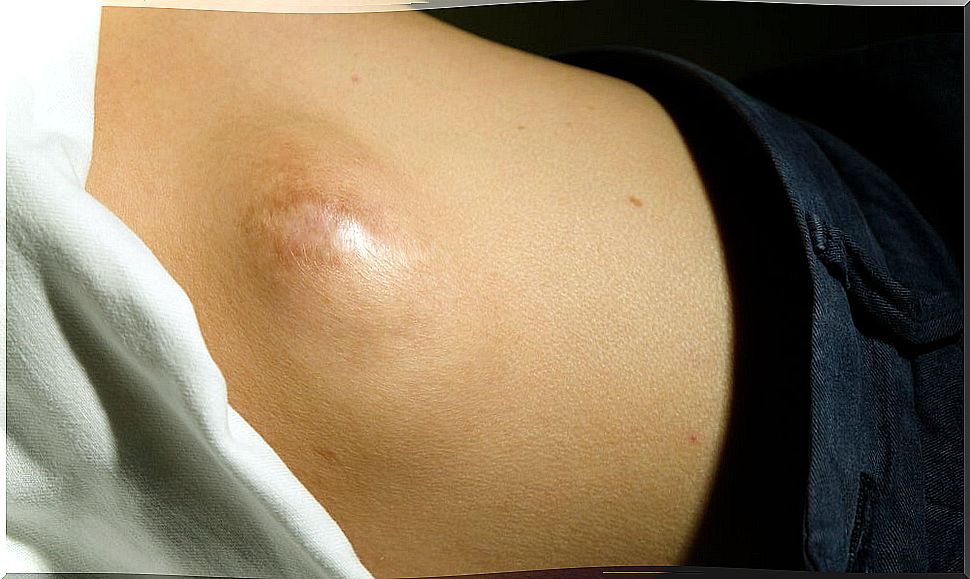
Symptoms
Sarcomas are usually not painful, unless they have advanced enough to press on a part of the body. Therefore, the diagnosis is difficult and suspicions take time to appear.
Another characteristic that determines that they do not manifest as many symptoms is that they can be located in deep regions. Being in depth, they take time to become apparent.
Perhaps the most common symptom is the appearance of a lump. It is usually the sign that determines the query. The palpable lump is not always due to the sarcoma itself, but can be a surrounding inflammation from tumor growth.
Sarcoma Diagnosis and Treatment
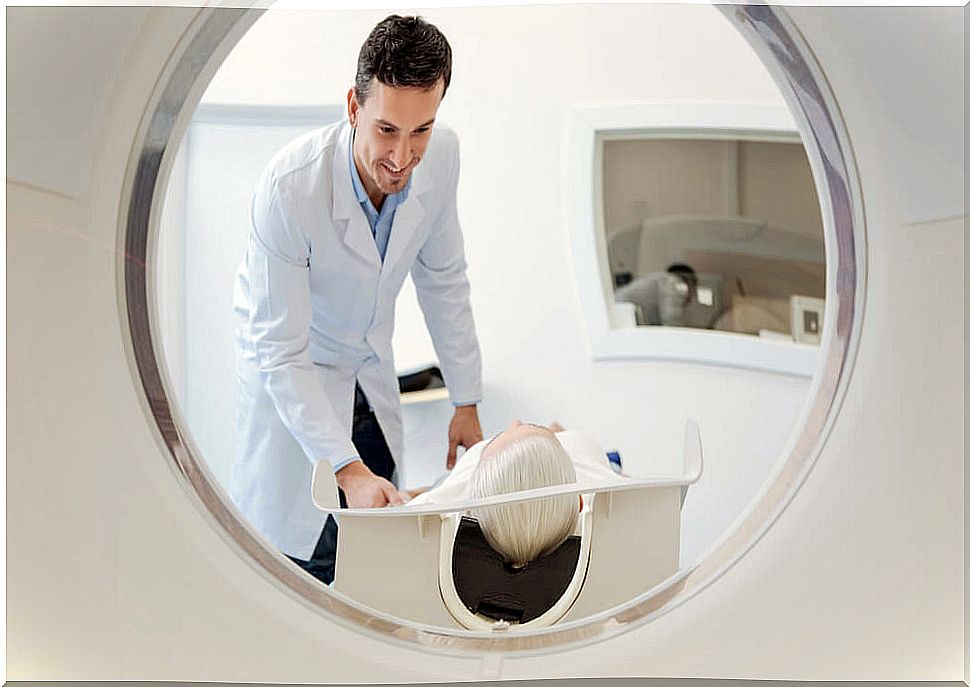
If the doctor suspects a sarcoma, he will order some imaging tests to initiate the diagnosis. An ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan may be ordered.
In case the images are suggestive of the presence of a neoplastic process, the next step is a biopsy. With the biopsy, the definitive diagnosis can be reached to confirm the sarcoma.

With the diagnosis confirmed, the therapeutic options are:
- Surgery: Many sarcomas can be surgically removed by solving the problem in this single step.
- Radiation therapy: the application of rays is usually an adjunct to surgery. If surgical resection could not remove the lesion with free edges is an indication.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is not always necessary for sarcomas. It is usually indicated in serious tumors or with complicated locations.
- Immunotherapy: relatively new, the use of biological drugs to fight cancer is promising. Immunotherapy seeks to slow down the process by which tumor cells block the body’s immune reaction. They are expensive drugs and are not available in everyone.
Is there to be alarmed?
The appearance of a lump anywhere on the body should be an alarm. It is necessary to consult a doctor so that the necessary and indicated complementary tests are carried out.
It is not about being alarmed at any lump under the skin, but it is about being vigilant. The delay in the consultation is capable of delaying the diagnosis and slowing down a treatment that could be totally effective for this cancer.