Medullary Aplasia: Everything You Need To Know
Medullary aplasia is a disease that affects the bone marrow. This is a spongy tissue found inside the long bones, vertebrae, pelvis, shoulder girdle, and others. It is responsible for the production of blood cells, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What happens in medullary aplasia is that the cells of the bone marrow that give rise to the different lines of blood cells disappear. Therefore, they all decrease. This can lead to anemia, an increased sensitivity to infection, and clotting problems.
Unfortunately, there are many circumstances that can trigger the disease. Treatment is essential, as it is a serious situation. In this article we explain everything you need to know about the disorder and how it is treated.
What is medullary aplasia?
Medullary aplasia is a disease of the bone marrow. It consists in the total or partial disappearance of the hematopoietic precursor cells.
These cells are what give rise to blood cells, such as red blood cells, leukocytes, and platelets. Therefore, when they are not present, there is a decrease in all these cell lines.
Blood cells are essential for life. Red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen to the tissues. Leukocytes are essential for the functioning of the immune system. Platelets (which are larger cell fragments) are responsible for the clotting process.
Medullary aplasia involves the dysfunction of all these functions. Therefore, it can lead to an anemic syndrome (called aplastic anemia ), bleeding, and infection.
Medullary aplasia can be partial or total, which makes its severity also variable. According to a study published in the Cuban Journal of Hematology, Immunology and Hemotherapy, it is estimated that the incidence is between 2 and 6 people per million inhabitants.
What are your causes?
Medullary aplasia can be caused by many situations. In general, the origins are divided into congenital or acquired.
The congenital is one that is present from birth. This group includes Fanconi anemia. It is a rare inherited disease that is transferred in an autosomal recessive manner. It causes a decrease in all types of blood cells.
On the other hand, as an article by the Josep Carreras Foundation explains, acquired causes are the most frequent. They are those in which hematopoietic stem cells disappear, either due to direct damage to the marrow or due to immune mechanisms.
In almost 80% of cases, the cause of the aplasia cannot be identified. For this reason it is said that it is an idiopathic form. Some of the etiologies that are usually identified are the following:
- Drugs or chemical agents: pesticides or benzene.
- Viral infections: hepatitis, human immunodeficiency virus, Epstein-Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus.
- Radiation and chemotherapy treatments: This is usually temporary.
Symptoms of spinal aplasia
As we pointed out at the beginning, spinal aplasia can be partial or total. In the partial there is still a small production of blood cells, so the symptoms may be somewhat milder than in the total.
Also, the signs vary depending on the affected cell line. According to the University of Navarra Clinic, if the production of red blood cells is affected, aplastic anemia will appear, which leads to fatigue, shortness of breath, pale skin and tachycardias. It is also usual that there is dizziness, vertigo or cramps.
When leukocytes are affected, what happens is that the patient has a very high susceptibility to infections. They are usually caused by rare germs and last longer than usual.
Finally, medullary aplasia may involve an alteration in platelet synthesis. They are the cellular fragments that intervene in the coagulation process. That is why it is usual for bleeding to appear.
How is it diagnosed?
To diagnose medullary aplasia, it is first important to know the patient’s medical history. It is essential to know if you have been undergoing any treatment, if you have other pathologies and what are your symptoms.
However, it requires certain complementary tests to confirm the diagnosis. Blood work is the key. Using this test, the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets can be quantified. In people with medullary aplasia, these cells will be below normal limits.
Another test that can aid diagnosis is a bone marrow biopsy. It consists of extracting a small sample of the marrow. It is usually done in the hip bone.
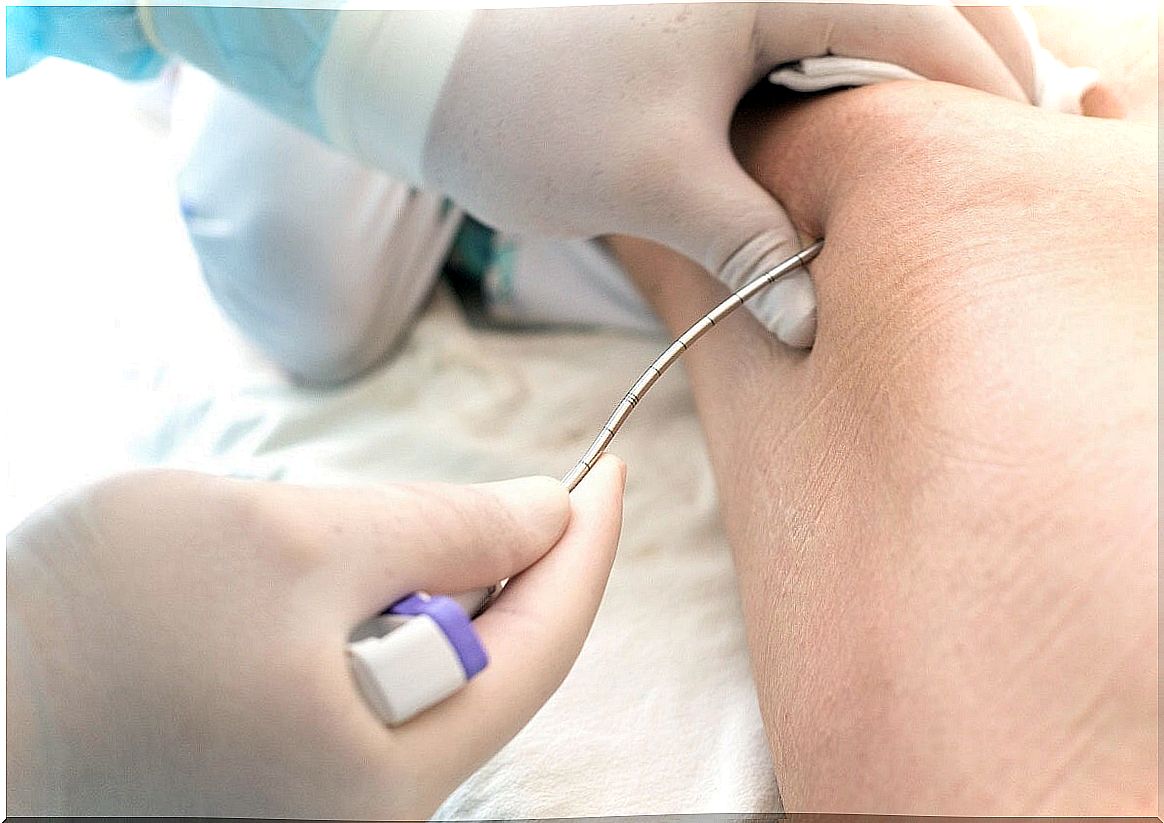
Medullary aplasia treatment options
Spinal aplasia can be life-threatening for those who suffer from it. When it comes to a serious case, it is usually necessary to hospitalize the patient.
One of the techniques that are usually used is blood transfusions. It is not a curative approach, but it can help control symptoms of anemia and bleeding. However, performing them repeatedly is associated with certain complications.
Another option is stem cell transplantation. As aplastic anemia consists of the deficiency of hematopoietic cells, this measure can help to generate new ones.
In any case, it is difficult to find compatible donors. In addition, the body can reject the transplant, which is life-threatening. This is a curative option, although it requires continuous immunosuppression of the patient and a long hospital stay.
Currently there are drugs that act as stimulants of the bone marrow. For example, filgrastim. They are drugs that are usually associated with immunosuppressants, such as cyclosporine.
Immunosuppressants are helpful if the cause of marrow aplasia is an alteration of the immune system. They also help maintain the patient until a bone marrow transplant is achieved.
Aplastic anemia is rare, but very serious
Aplastic anemia is a serious disease that causes a decrease in blood cells. There are many causes that can lead to this pathology. However, in a large percentage of patients the exact reason why it has occurred is not found.
The problem is that these people can suffer from severe anemia, clotting problems, and frequent and long-term infections. Therefore, it is important to establish a treatment as soon as possible. Otherwise, the person is at serious risk of death.