Tips To Avoid Altitude Sickness
Altitude sickness is a condition conditioned by several factors, such as the person’s physical preparation before climbing, their diet or age, among others. Learn more in this post.

Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS), altitude sickness or altitude sickness is a set of symptoms such as nausea, dizziness and exhaustion, which occur when an individual faces altitude levels to which their body is not accustomed.
The elements that cause this discomfort are the decrease in atmospheric pressure and the lack of oxygen, factors to which the body cannot adapt immediately and tries to react to compensate.
If the changes occur faster than our body can react, the acclimatization process will be obstructed and it will begin to fail, which will inevitably cause problems.
Normally, the human body begins to be affected when it is 2,400 meters above sea level. However, a person can withstand a height of up to 8,000 meters.
It is not impossible to live in high mountains, the body only needs a little time to get used to transporting more blood cells and thus improving the flow of oxygen throughout the body.
For example, people who live in mountainous regions and those who engage in sports such as mountaineering resist discomfort due to altitude, as their body has overcome acclimatization.
Another point to consider is that the faster the ascent, the more severe the disorder. And as you go up, less oxygen receives the brain.
Causes of altitude sickness

The causes of Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS) can originate for various reasons, among these are the following:
1. Precipitous ascent
Faster does not always mean better, when you ascend precipitously the body has no possibility of acclimatizing, it often happens when you go up long distances in a vehicle.
2. Not having adequate physical preparation
If a person has never climbed a mountain before in his life, when he is above 2,000 meters he will begin to feel discomfort much earlier than his companions. This case occurs mainly in excursions formed by inexperienced young people who are starting in the world of mountaineering.
3. Bad diet

To perform any physical activity it is necessary to receive enough energy, this is achieved with food. Therefore, a poor diet or hydration makes it difficult for the body to acclimatise.
4. Be under 50 years old
Although it sounds strange, it is at this age that humans have a mature nervous system. People under 50 years of age are more likely to suffer from altitude disorders.
Symptoms of altitude sickness
The symptoms of AMS can range from mild to severe:
Mild
- Difficulty getting to sleep.
- Dizziness or feeling dizzy
- Fatigue.
- Headache.
- Lack of appetite.
Moderate

- Nausea or vomiting
- Rapid pulse (increased heart rate).
- Shortness of breath or dyspnea.
Serious
- Bluish discoloration of the skin (cyanosis).
- Chest stiffness or engorgement.
- Confusion or lightheadedness
- Regular or bleeding cough.
- Decreased state of consciousness.
- Inability to walk
- Asthma.
Natural remedies to counteract altitude sickness
1. Celery juice
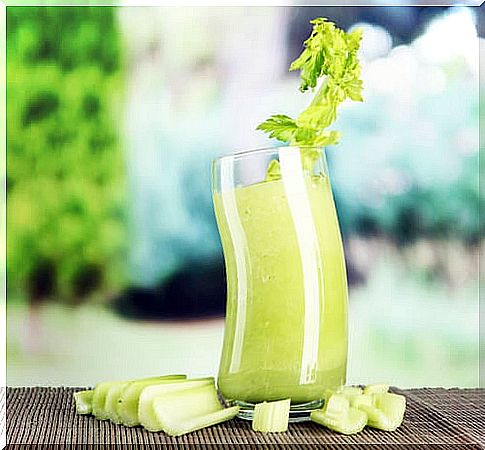

Ingredients
- 3 stalks of celery.
- 1 cup of water (100ml).
Preparation
- Blend celery or run it through the juicer and refrigerate it.
- Carry it in a backpack during the trip.
When you experience dizziness or start to feel weak, drink half a glass and save the rest. This shake is intended to combat the feeling of vertigo produced by low blood pressure in the body.
2. Ginger water
Ingredients
- Ginger extract.
- 200 ml of water.
Preparation
- Put 20 drops of ginger extract in a dropper.
- Then add them to the 200 ml of water.
Consume slowly in case of dizziness. It also helps to chew an inch of ginger root as it climbs, like chewing gum.
3. Lemon soda

Ingredients
- Juice of one lemon.
- 1 glass of water (200ml).
Preparation
- Squeeze a lemon and pour its juice into the glass with water.
Drink slowly so that the stomach assimilates it. Lemon acid calms the stomach lining, reducing the possibility of vomiting. It also prevents dehydration and alkalizes the body.
Finally, to counteract the symptoms and help the body to adapt, days before it is recommended not to consume alcohol, hydrate well and eat foods rich in carbohydrates.